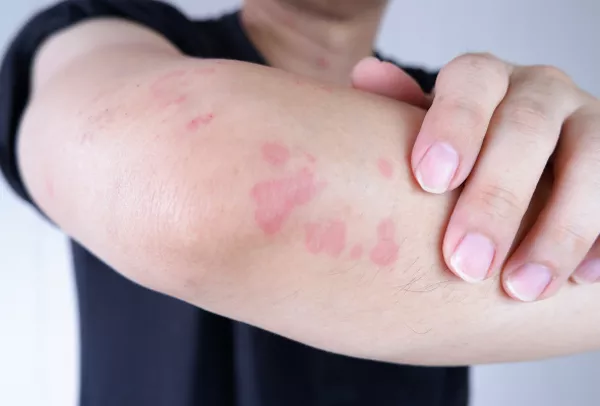
Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, can manifest in various forms and affect different parts of the body. Among the many areas susceptible to eczema, the back of the knees is a common site for this uncomfortable and often itchy condition. Understanding the triggers and causes behind eczema on the back of knees is crucial for effective management and treatment. In this article, we delve into the complexities of eczema, exploring its underlying causes, aggravating factors, and potential treatment options.
What is Eczema?
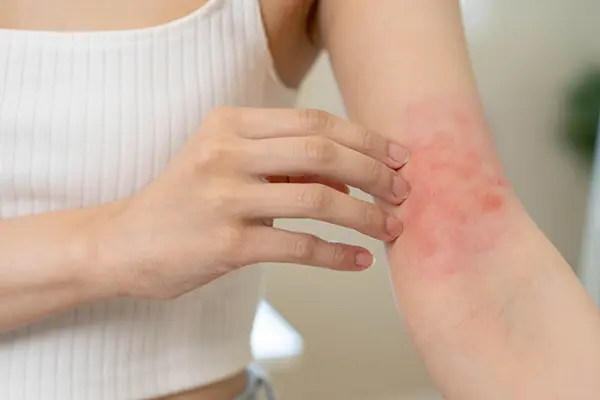
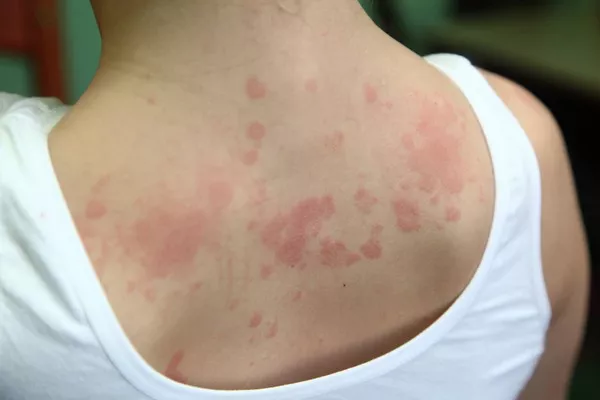
Before diving into the specifics of eczema on the back of knees, it’s essential to grasp the basics of this skin condition. Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is characterized by inflamed, red, and itchy skin. It often presents with a combination of symptoms, including dryness, scaling, and sometimes blistering. Eczema can vary in severity, ranging from mild occasional flare-ups to chronic and debilitating conditions.
The Back of Knees: A Vulnerable Site for Eczema
The skin on the back of knees is particularly vulnerable to eczema due to several factors. Firstly, this area tends to experience increased moisture and warmth, especially in individuals who sweat excessively or wear tight clothing. Additionally, the skin folds behind the knees can create friction and irritation, exacerbating existing skin conditions like eczema.
Genetic Predisposition
One of the primary factors contributing to eczema is genetics. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies are more likely to develop the condition. Genetic mutations affecting the skin barrier function and immune response can increase susceptibility to eczema and other inflammatory skin disorders.
Impaired Skin Barrier Function
The skin acts as a protective barrier against external irritants and allergens. In eczema, this barrier function is compromised, allowing irritants to penetrate the skin more easily and triggering inflammatory responses. Factors such as harsh soaps, detergents, and environmental pollutants can further weaken the skin barrier, leading to eczema flare-ups.
Immune System Dysfunction
Another underlying cause of eczema is immune system dysfunction. In individuals with eczema, the immune system overreacts to certain triggers, causing inflammation and skin irritation. This immune dysregulation can be influenced by genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and alterations in the skin microbiome.
Allergens and Irritants
Exposure to allergens and irritants plays a significant role in triggering eczema flare-ups. Common allergens include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and certain foods. Irritants such as harsh chemicals, fragrances, and fabrics can also exacerbate eczema symptoms. The back of knees, being in close contact with clothing and environmental allergens, is particularly susceptible to irritation and inflammation.
Climate and Environmental Factors
Climate and environmental factors can influence the prevalence and severity of eczema. Dry and cold weather can lead to skin dehydration and exacerbate eczema symptoms, while hot and humid conditions may increase sweat production and skin irritation. Additionally, exposure to UV radiation from sunlight can either improve or worsen eczema symptoms, depending on individual sensitivity and skin type.
Stress and Psychological Factors
Stress and psychological factors can contribute to eczema flare-ups by triggering immune system responses and disrupting the skin barrier function. High levels of stress can lead to increased inflammation and cortisol production, which may exacerbate eczema symptoms. Moreover, the psychological impact of living with a chronic skin condition like eczema can further exacerbate stress levels, creating a vicious cycle of inflammation and symptom aggravation.
Treatment and Management Strategies
While eczema on the back of knees can be challenging to manage, several treatment options and lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
1. Moisturization: Keeping the skin well-hydrated with emollients and moisturizers can help restore the skin barrier function and reduce dryness and itching.
2. Topical Steroids: Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching associated with eczema flare-ups. These medications should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize side effects.
3. Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as allergens, irritants, and certain foods can help prevent eczema flare-ups.
4. Proper Skincare: Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products and avoiding harsh soaps and detergents can help maintain the skin barrier function and prevent irritation.
5. Stress Management: Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help reduce stress levels and minimize eczema flare-ups.
6. Medical Treatments: In severe cases of eczema, systemic medications such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic agents may be prescribed to control inflammation and improve symptoms.
7. Phototherapy: Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. This treatment can help reduce inflammation and improve eczema symptoms, especially in individuals with moderate to severe eczema.
Conclusion
Eczema on the back of knees can be a source of discomfort and frustration for those affected by this chronic skin condition. By understanding the triggers and underlying causes of eczema, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Through a combination of proper skincare, avoidance of triggers, stress management, and medical treatments, eczema sufferers can find relief and achieve long-term control over their condition. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and preferences. With the right approach, eczema on the back of knees can be effectively managed, allowing individuals to enjoy healthier, happier skin.