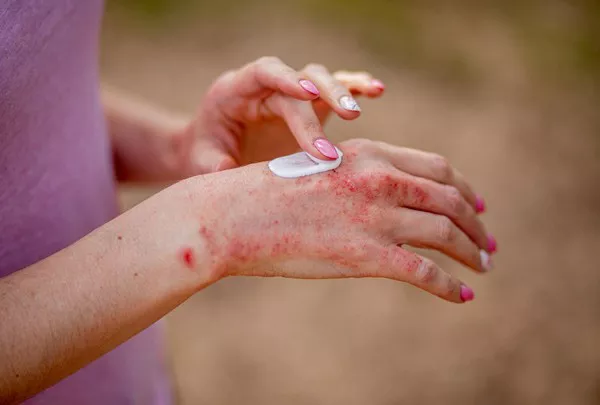
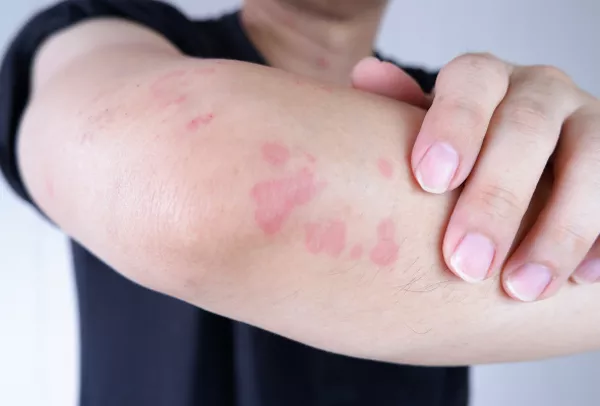
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, dryness, and itching. One of the distressing symptoms experienced by individuals with eczema is the development of blisters on the hands. These blisters can be painful, itchy, and may lead to skin damage if not managed properly. Fortunately, there are several strategies that can help prevent and alleviate eczema blisters on the hands. By implementing a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and medical interventions, individuals can gain better control over this challenging aspect of their condition.
Understanding Eczema Blisters
Eczema blisters, also known as dyshidrotic eczema or pompholyx, typically appear on the palms of the hands, fingers, and soles of the feet. They are small, fluid-filled lesions that can cause intense itching and discomfort. The exact cause of eczema blisters is not fully understood, but they are believed to be triggered by factors such as stress, allergens, irritants, or changes in weather conditions. People with a history of allergies, asthma, or other forms of eczema are more prone to developing these blisters.
Preventive Measures
Preventing eczema blisters on the hands requires a multifaceted approach that addresses triggers, maintains skin health, and promotes overall well-being. Here are key preventive measures to consider:
1. Identify and Avoid Triggers: Keep a journal to track activities, foods, or environments that exacerbate your eczema symptoms. Common triggers include exposure to irritants like harsh soaps or detergents, allergens like certain metals or fabrics, stress, and extremes in temperature. Minimizing exposure to these triggers can significantly reduce the occurrence of blisters.
2. Adopt Gentle Skincare Practices: Use mild, fragrance-free soaps and moisturizers to cleanse and hydrate your hands. Avoid hot water and opt for lukewarm temperatures when washing your hands, as hot water can strip away natural oils and worsen eczema symptoms.
3. Moisturize Regularly: Keep your hands well moisturized throughout the day, especially after washing. Choose emollient-rich creams or ointments that help lock in moisture and protect the skin barrier. Apply moisturizer several times a day, focusing on areas prone to blisters.
4. Wear Protective Gloves: When engaging in activities that involve exposure to irritants or water, such as washing dishes or cleaning, wear protective gloves to shield your hands from potential triggers.
5. Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms, including the formation of blisters. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to promote relaxation and overall skin health.
6. Avoid Scratching: Although eczema blisters can be intensely itchy, avoid scratching them as this can lead to further irritation, infection, and skin damage. Keep your nails short and consider using anti-itch creams or cold compresses to relieve itching.
Medical Interventions
In addition to lifestyle modifications, medical interventions may be necessary to manage eczema blisters effectively:
1. Topical Corticosteroids: Your dermatologist may prescribe topical corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of eczema blisters. Use these medications as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
2. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: In cases where corticosteroids are not suitable or effective, topical calcineurin inhibitors may be recommended to help control eczema symptoms and prevent blister formation.
3. Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light. This treatment can help reduce inflammation and itching associated with eczema blisters.
4. Systemic Medications: For severe cases of eczema that do not respond to topical treatments, systemic medications such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologics may be considered. These medications require close monitoring by a healthcare provider due to potential side effects.
Conclusion
Managing eczema blisters on the hands requires a comprehensive and individualized approach that addresses triggers, promotes skin health, and utilizes appropriate medical interventions when necessary. By implementing preventive measures and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can minimize the occurrence and impact of eczema blisters, leading to improved quality of life and skin comfort. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms despite these strategies, consult a dermatologist or allergist for personalized evaluation and treatment. With proactive management, it is possible to achieve better control over eczema and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin.
Related Topics: