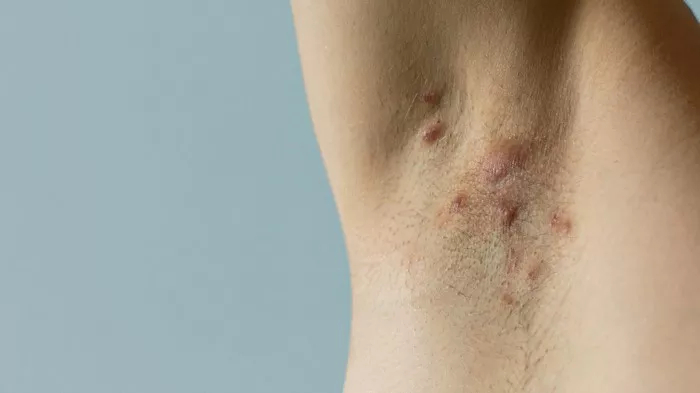
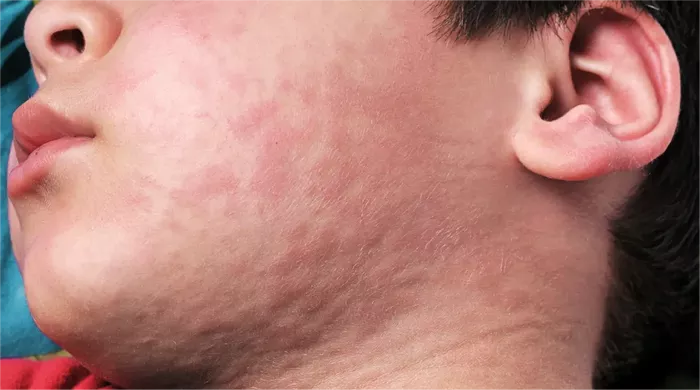
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by painful, inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts, predominantly occurring in areas where skin rubs together. Understanding the duration and management of HS flare-ups is crucial for those affected by this condition. This article delves into the factors influencing the duration of HS flare-ups, the typical timeline, and effective strategies for managing and minimizing these episodes.
Understanding Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory condition of the hair follicles, primarily affecting areas such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. The exact cause of HS is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. HS can be debilitating, significantly impacting the quality of life of those affected.
Factors Influencing the Duration of HS Flare-Ups
Several factors can influence the duration of an HS flare-up, including:
Severity of the Condition
HS can range from mild to severe, with the severity influencing the duration and intensity of flare-ups. Mild cases may experience shorter and less frequent flare-ups, while severe cases may have prolonged and more intense episodes.
Stage of the Disease
HS progresses through different stages, from early lesions to more severe chronic abscesses and sinus tracts. The stage of the disease can impact the duration of flare-ups, with later stages often resulting in longer and more persistent symptoms.
Treatment and Management
Effective treatment and management strategies play a crucial role in controlling HS flare-ups. Proper medical intervention, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to treatment plans can significantly reduce the duration and frequency of flare-ups.
Individual Variability
Each individual’s experience with HS can vary significantly. Factors such as overall health, immune system function, and personal response to treatments can influence the duration of flare-ups.
Typical Timeline of HS Flare-Ups
While the duration of HS flare-ups can vary widely among individuals, there are general patterns observed in the progression of these episodes.
Initial Onset
The initial onset of an HS flare-up is often marked by the appearance of tender, inflamed nodules or abscesses. This phase can last from a few days to a week, depending on the severity and the effectiveness of early intervention.
Progression
As the flare-up progresses, the nodules may enlarge, become more painful, and sometimes rupture, releasing pus. This phase can last from several days to a few weeks. The formation of sinus tracts and chronic abscesses can prolong this stage.
Healing
The healing phase of an HS flare-up can vary significantly. In mild cases, the nodules and abscesses may resolve within a week or two, while more severe cases can take several weeks to months to heal completely. Scarring is common in the healing phase, particularly in more advanced stages of the disease.
Effective Strategies for Managing HS Flare-Ups
Managing HS flare-ups effectively requires a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and self-care strategies.
Medical Treatments
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to reduce bacterial infection and inflammation. They can help shorten the duration of flare-ups and prevent secondary infections.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce pain and inflammation during flare-ups.
Biologics
Biologic medications, such as adalimumab, target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups. These medications are often used for moderate to severe cases of HS.
Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal therapy, including oral contraceptives and anti-androgens, can be effective for some individuals, particularly women, in managing HS flare-ups.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to drain abscesses, remove sinus tracts, or excise affected areas of skin. Surgical treatment can help reduce the duration and recurrence of flare-ups.
Lifestyle Modifications
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce friction and pressure on areas prone to HS, potentially decreasing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking is a known risk factor for HS. Quitting smoking can significantly improve the overall management of the condition and reduce the duration of flare-ups.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help manage inflammation and support overall health.
SEE ALSO: How Does Hidradenitis Suppurativa Spread?
Self-Care Strategies
Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene, including regular cleansing of affected areas with gentle, non-irritating cleansers, can help prevent infections and reduce the severity of flare-ups.
Stress Management
Stress is known to exacerbate HS flare-ups. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and relaxation exercises, can help mitigate the impact of stress on the condition.
Clothing Choices
Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing can reduce friction and irritation in areas prone to HS, potentially minimizing the duration and severity of flare-ups.
Psychological Impact and Support
HS can have a significant psychological impact on individuals, leading to feelings of embarrassment, depression, and anxiety. Seeking support from mental health professionals, support groups, or online communities can provide emotional support and coping strategies.
Support Groups and Online Communities
Connecting with others who have HS can provide valuable support, shared experiences, and practical tips for managing flare-ups. Online communities and local support groups can offer a sense of belonging and understanding.
Mental Health Professionals
Counseling or therapy with a mental health professional can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of living with HS. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can be beneficial.
Future Directions and Research
Ongoing research into the underlying causes and treatment of HS is crucial for improving the management and duration of flare-ups. Advances in understanding the genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors contributing to HS can lead to more targeted and effective treatments.
Clinical Trials
Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new and potentially more effective treatments for HS. Discussing clinical trial options with a healthcare provider can be a valuable step for individuals seeking alternative treatments.
Genetic Research
Genetic research aims to identify specific genetic markers associated with HS, which can lead to personalized treatment approaches and better understanding of the disease’s progression.
Novel Therapies
Emerging therapies, such as laser treatments, photodynamic therapy, and novel biologic agents, hold promise for improving the management and duration of HS flare-ups. Ongoing research and clinical studies are essential for validating the effectiveness of these treatments.
Conclusion
The duration of HS flare-ups can vary widely among individuals, influenced by factors such as disease severity, stage, treatment, and individual variability. While mild cases may resolve within a few days to weeks, more severe flare-ups can last for several weeks to months. Effective management strategies, including medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and self-care practices, are essential for reducing the duration and frequency of flare-ups. Ongoing research and support from healthcare professionals and communities play a crucial role in improving the quality of life for individuals living with HS.
Related Topics: