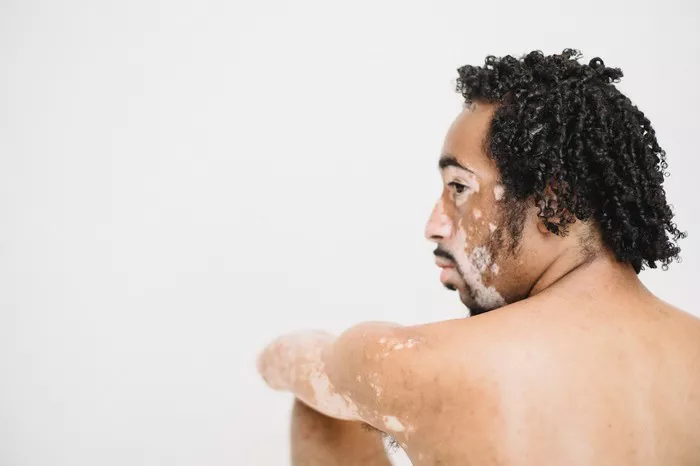
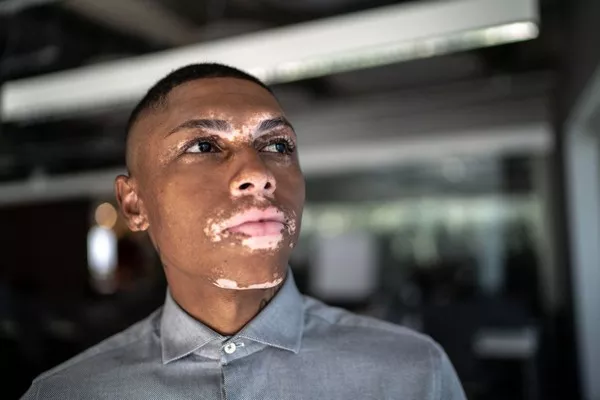
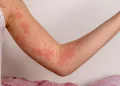
Vitiligo is a condition that affects the pigmentation of the skin, resulting in the loss of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes. This loss leads to the development of white patches on various parts of the body. While vitiligo is primarily known for its effects on the skin, it can also affect hair, leading to what is commonly referred to as “vitiligo hair.” This article delves into the phenomenon of vitiligo hair, its causes, implications, and potential treatments.
The Mechanism Behind Vitiligo Hair
Vitiligo hair occurs when the hair follicles lose their melanocytes, similar to what happens in the skin. Melanocytes are critical for the production of melanin, the pigment that gives hair its color. When these cells are destroyed or become non-functional due to vitiligo, the hair growing from the affected follicles turns white or gray. This depigmentation can occur on any part of the body where hair grows, including the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, and body hair.
Causes of Vitiligo Hair
The exact cause of vitiligo remains unknown, but several theories have been proposed. The primary theories include:
1. Autoimmune Hypothesis: This is the most widely accepted theory. It suggests that vitiligo is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys melanocytes. This destruction leads to the depigmentation seen in both skin and hair.
2. Genetic Factors: Vitiligo often runs in families, indicating a genetic predisposition. Specific genes have been linked to the condition, although the exact genetic mechanisms are not fully understood.
3. Environmental Triggers: Certain environmental factors, such as stress, exposure to harmful chemicals, or skin trauma, may trigger vitiligo in genetically susceptible individuals.
4. Neurogenic Factors: Some researchers suggest that neurochemical factors released by nerve endings in the skin might contribute to melanocyte destruction.
Symptoms and Identification of Vitiligo Hair
Vitiligo hair is characterized by the appearance of white or gray hair in localized patches on the scalp or other hair-bearing areas. The extent and distribution of vitiligo hair can vary widely among individuals. In some cases, it may be limited to a few strands of hair, while in others, larger patches of hair may be affected.
Common symptoms include:
- White or Gray Hair Patches: The most obvious sign is the development of white or gray patches of hair. These patches often correspond to the depigmented areas of skin affected by vitiligo.
- Skin Depigmentation: Vitiligo hair is often accompanied by depigmented patches of skin. The presence of both skin and hair depigmentation in the same area can help in diagnosing vitiligo hair.
- Symmetry: Vitiligo often appears symmetrically, affecting both sides of the body. This pattern can also be seen in vitiligo hair.
Psychological and Social Impact
The appearance of vitiligo hair, particularly when it affects visible areas such as the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes, can have significant psychological and social impacts. Individuals with vitiligo hair may experience:
- Self-Esteem Issues: Changes in appearance due to vitiligo hair can affect self-esteem and body image, leading to feelings of self-consciousness or embarrassment.
- Social Anxiety: The visible nature of vitiligo hair can lead to social anxiety, as individuals may feel uncomfortable in social situations or fear negative judgment from others.
- Emotional Distress: Coping with a chronic condition like vitiligo can be emotionally challenging, and the additional burden of hair depigmentation can exacerbate feelings of distress or frustration.
Diagnosis of Vitiligo Hair
Diagnosing vitiligo hair involves a thorough examination by a dermatologist or healthcare professional. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Clinical Examination: A visual inspection of the affected areas to identify characteristic signs of vitiligo, such as white patches of skin and hair.
- Medical History: Gathering information about the patient’s medical history, including any family history of vitiligo or other autoimmune conditions.
- Wood’s Lamp Examination: Using a special ultraviolet light (Wood’s lamp) to highlight depigmented areas that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis by examining the presence or absence of melanocytes in the affected area.
SEE ALSO: What Causes Patchy Loss of Skin Pigmentation
Treatment Options for Vitiligo Hair
While there is no cure for vitiligo, various treatment options can help manage the condition and improve the appearance of vitiligo hair. These treatments include:
1. Topical Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications can be applied to the affected areas to help reduce inflammation and potentially stimulate repigmentation. They are often used in the early stages of vitiligo.
2. Topical Immunomodulators: Medications such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can be applied to the skin to modulate the immune response and promote repigmentation.
3. Phototherapy: Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy is a common treatment for vitiligo. It involves exposing the affected skin to specific wavelengths of ultraviolet light to stimulate melanocyte activity and encourage repigmentation.
4. Excimer Laser: This targeted form of phototherapy uses a laser to deliver high-intensity UVB light to small, localized areas of depigmented skin and hair.
5. Micropigmentation (Medical Tattooing): This cosmetic procedure involves tattooing the depigmented areas with pigments that match the surrounding skin or hair color. It can help camouflage vitiligo hair and improve appearance.
6. Hair Dye: For individuals with vitiligo hair on the scalp, eyebrows, or beard, using hair dye can be a simple and effective way to mask the white or gray hair and achieve a more uniform appearance.
7. Wigs and Hairpieces: For those with extensive vitiligo hair on the scalp, wigs or hairpieces can provide a practical solution for restoring a natural look.
Living with Vitiligo Hair
Managing vitiligo hair involves not only addressing the physical aspects of the condition but also coping with its emotional and social impacts. Here are some strategies for living with vitiligo hair:
1. Education and Awareness: Learning about vitiligo and understanding its nature can help individuals and their families cope better with the condition. Awareness campaigns and support groups can provide valuable information and emotional support.
2. Seeking Support: Joining support groups or connecting with others who have vitiligo can be beneficial. Sharing experiences and coping strategies can help reduce feelings of isolation and provide a sense of community.
3. Counseling and Therapy: Professional counseling or therapy can be helpful for individuals struggling with the emotional and psychological aspects of vitiligo hair. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can assist in building self-esteem and coping skills.
4. Cosmetic Solutions: Exploring cosmetic options such as hair dye, makeup, or micropigmentation can help improve appearance and boost confidence.
5. Sun Protection: Depigmented skin is more susceptible to sunburn, so using sunscreen and protective clothing is essential to prevent sun damage.
6. Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can support overall well-being and potentially improve the body’s response to treatments.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research into the causes and treatment of vitiligo continues to advance our understanding of the condition and holds promise for the future. Some areas of research and potential future directions include:
1. Genetic Studies: Identifying specific genes associated with vitiligo could lead to targeted therapies and personalized treatment approaches.
2. Stem Cell Therapy: Research into the use of stem cells to regenerate melanocytes and restore pigmentation is an exciting area of exploration.
3. Immunotherapy: Developing new immunomodulatory treatments to regulate the immune response and prevent melanocyte destruction is a key focus.
4. Combination Therapies: Investigating the effectiveness of combining different treatment modalities, such as phototherapy and topical medications, to enhance repigmentation outcomes.
Conclusion
Vitiligo hair is a manifestation of the broader condition of vitiligo, characterized by the loss of melanocytes in hair follicles leading to white or gray hair. While it can have significant psychological and social impacts, various treatment options and coping strategies are available to manage the condition and improve quality of life. Ongoing research continues to shed light on the underlying mechanisms of vitiligo and holds promise for more effective treatments in the future. By understanding and addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of vitiligo hair, individuals can navigate the challenges of this condition with greater confidence and resilience.
Related Topics: