Histamine rash, often characterized by its sudden appearance and itchy, red welts on the skin, can be a perplexing and uncomfortable condition. This rash is the result of histamine, a chemical involved in the body’s immune response, being released inappropriately or excessively. Histamine plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including inflammatory responses and allergic reactions. When histamine is released in excess, it can lead to a variety of skin symptoms, collectively referred to as histamine rash or urticaria. This condition can range from acute episodes lasting a few hours to chronic issues persisting for months or even years.
Definition & Basics
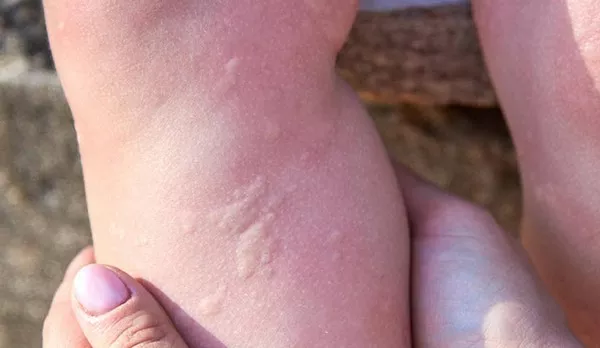
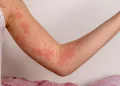
Histamine rash, or urticaria, occurs when the immune system releases histamine, a chemical involved in allergic reactions and inflammation. Histamine causes the blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable, leading to the formation of welts on the skin. These welts are typically red, raised, and itchy, and they can appear anywhere on the body.
Symptoms
The hallmark symptoms of histamine rash include:
Welts: Raised, red bumps on the skin.
Redness: The affected area may appear red or pink.
Swelling: The skin can swell, often in the form of larger areas or patches.
Itching: The rash is usually very itchy, leading to discomfort.
Causes
Allergic Reactions
Food Allergens: Common food allergens include nuts, shellfish, dairy, and eggs. These allergens can provoke a histamine response, leading to a rash.
Insect Bites/Stings: Venom from insect bites or stings (e.g., bees, wasps) can cause a significant release of histamine, resulting in localized or widespread rashes.
Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can trigger histamine release in some individuals.
Latex: Latex allergies are another common cause of histamine rash. Exposure to latex products can provoke an allergic reaction that includes histamine release.
Other Triggers
Several non-allergic factors can also induce histamine rash:
Cold: Exposure to cold temperatures, such as from cold weather or ice packs, can cause a condition known as cold urticaria, where histamine is released in response to the cold.
Sun: Sun exposure can trigger a rash in some people, known as solar urticaria, which is caused by histamine release in response to UV radiation.
Stress/Anxiety: Emotional factors like stress and anxiety can lead to the release of histamine, which may result in a rash.
Exercise: Physical exertion can cause exercise-induced urticaria, where intense exercise leads to histamine release and subsequent rash.
Infection: Certain infections can trigger histamine reactions as part of the body’s immune response.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions can influence histamine release:
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the immune system and lead to increased histamine release.
Chronic Urticaria: This is a long-term condition where hives persist for more than six weeks. It may be idiopathic (unknown cause) or linked to other health issues.
SEE ALSO: The 5 Best Over-the-Counter Antihistamines for Hives
Diagnosis & Treatment
Seeking Medical Help
Allergy Testing
Allergy testing can help identify specific triggers for histamine rash. Tests may include skin prick tests, blood tests, or elimination diets to determine the allergens responsible.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are the primary treatment for histamine rash. They work by blocking histamine receptors, reducing itching, swelling, and redness. Both over-the-counter and prescription antihistamines are available. Common options include cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments such as corticosteroid creams can help alleviate symptoms by reducing inflammation. However, their effectiveness may be limited compared to systemic treatments.
Lifestyle Modifications
To manage and prevent histamine rash, consider these lifestyle changes:
Avoiding Triggers: Identify and avoid known allergens or triggers, such as specific foods or environmental factors.
Stress Management: Practice stress-relief techniques, such as meditation or exercise, to reduce emotional triggers.
Proper Skin Care: Use gentle, fragrance-free skin care products to avoid irritating the skin.
Conclusion
Understanding histamine rash involves a comprehensive approach to recognizing its causes, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment. This condition, while often uncomfortable and distressing, can be managed successfully with the right strategies. By identifying specific triggers and employing targeted therapies, individuals can achieve significant relief from the symptoms of histamine rash. It is essential for those experiencing persistent or severe symptoms to seek medical advice, as a thorough evaluation can help tailor treatment plans and improve qual
Related Topics: