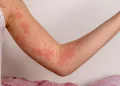
Stress is a common part of life, but for some people, it can manifest physically in the form of hives, a condition also known as urticaria. Stress hives are not only uncomfortable but can also be a source of concern, especially if they occur frequently. Understanding how stress hives happen can help you manage and prevent them effectively.
Understanding Urticaria
Urticaria, more commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of red, itchy, and swollen welts or bumps on the skin. These welts can vary in size and can appear anywhere on the body, sometimes merging to form larger patches.
Hives are the result of the body’s immune system responding to a perceived threat by releasing chemicals such as histamine. This release causes the small blood vessels in the skin to leak, leading to the characteristic swelling and redness. Urticaria can be acute, lasting less than six weeks, or chronic, persisting for more extended periods or recurring frequently.
While these hormones are essential for survival, chronic stress can lead to a dysregulated immune response. Prolonged stress can cause the immune system to become overactive or underactive, leading to various health issues, including the development of hives. The immune system, in its heightened state, may mistakenly target the body’s tissues, including the skin, leading to the release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals that cause hives.
Stress-Induced Urticaria
Stress hives, also known as stress-induced urticaria, are hives that are specifically triggered by psychological stress. While the exact mechanism behind stress hives is not fully understood, it is believed to involve a complex interaction between the nervous system, immune system, and skin.
When a person experiences stress, the nervous system can stimulate the release of histamine and other chemicals in the skin. This response can lead to the rapid appearance of hives, which may occur suddenly and can be either short-lived or persistent. Stress hives can be frustrating because they often seem to appear out of nowhere and may disappear just as quickly, making them difficult to predict or prevent.
How Stress Triggers Hives
The process by which stress triggers hives is multifaceted. Stress can cause the release of histamine from mast cells, which are specialized cells in the skin that play a crucial role in allergic reactions and inflammation. When histamine is released, it causes the blood vessels in the skin to dilate and become more permeable, leading to the swelling, redness, and itching characteristic of hives.
In addition to direct histamine release, stress can exacerbate existing allergies or sensitivities. For individuals who are already prone to allergic reactions, stress can make them more susceptible to developing hives in response to allergens that they might typically tolerate. This heightened sensitivity can make managing hives more challenging, as stress not only triggers the condition but can also worsen it.
Identifying Triggers
Understanding what triggers your stress hives is a crucial step in managing them. Common stress triggers include:
Work Pressure: High demands at work, tight deadlines, or conflicts with colleagues can all contribute to stress that may trigger hives.
Relationship Problems: Issues in personal relationships, whether with a partner, family members, or friends, can lead to significant emotional stress.
Financial Difficulties: Money-related concerns, such as debt, job insecurity, or unexpected expenses, can be a major source of stress.
Major Life Changes: Events such as moving, changing jobs, or experiencing a loss can cause stress that may manifest as hives.
Anxiety and Depression: Underlying mental health conditions like anxiety and depression can also contribute to stress-induced hives.
By identifying your specific stress triggers, you can begin to develop strategies to avoid or manage them. Keeping a journal of when hives occur and the circumstances surrounding their appearance can help you pinpoint what triggers them.
SEE ALSO: Can You Get Hives from Nerves?
Managing Stress-Related Hives
While it may not always be possible to eliminate stress entirely, there are several strategies you can employ to reduce its impact and manage stress-related hives:
Mindfulness Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help calm the nervous system and reduce stress levels, which may prevent hives from developing.
Relaxation Exercises: Regular relaxation exercises, such as progressive muscle relaxation or yoga, can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
Regular Physical Activity: Exercise is a proven way to reduce stress and improve mood. Engaging in regular physical activity can help keep stress levels in check and reduce the likelihood of hives.
Adequate Sleep: Ensuring that you get enough sleep is essential for managing stress. Lack of sleep can exacerbate stress and make the body more susceptible to hives.
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and help the body cope with stress more effectively.
Conclusion
Stress hives, or stress-induced urticaria, are a physical manifestation of psychological stress, resulting from the complex interplay between the nervous system, immune system, and skin. While stress is a natural part of life, it is essential to manage it effectively to prevent hives and other stress-related health issues. By understanding your triggers and adopting stress-reducing strategies, you can minimize the impact of stress hives on your life. However, if hives persist or significantly interfere with your daily activities, seeking medical advice is crucial to ensure proper management and treatment.
Related Topics: