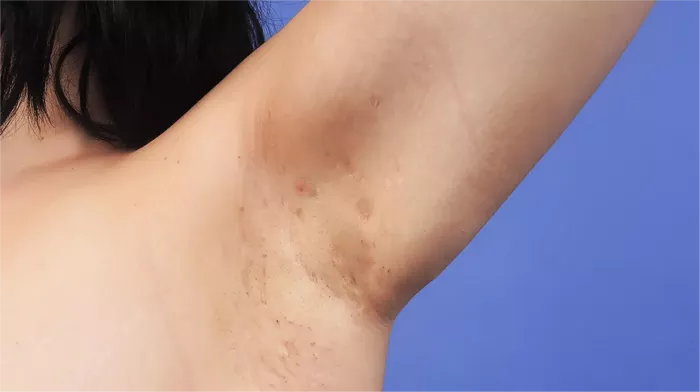
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by the formation of painful, inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts, primarily in areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. The condition typically begins after puberty and can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Pain in HS is a common and distressing symptom, manifesting in various ways. Patients often experience localized pain, tenderness, and general discomfort in the affected areas. This pain can range from mild to severe and may interfere with daily activities and overall well-being.
SEE ASLO: What Foods Cause Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Inflammatory Process
The inflammatory process in hidradenitis suppurativa is a major contributor to the pain experienced by patients. Inflammation occurs when the body’s immune system responds to perceived threats, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other mediators. This response results in swelling, redness, and heat in the affected areas. In HS, inflammation primarily affects the hair follicles and nearby skin tissues, causing them to become swollen and tender. The inflammatory response not only contributes to the pain but also exacerbates other symptoms of the condition.
Formation of Abscesses and Nodules
The formation of abscesses and nodules is central to the pain experienced in hidradenitis suppurativa. These painful lesions occur when blocked hair follicles become inflamed and filled with pus. Over time, the buildup of pus and inflammation leads to the formation of abscesses that can rupture and cause further pain. The nodules, often deep and painful, can be particularly distressing due to their size and location. The pressure from these lesions on surrounding tissues contributes significantly to the discomfort and pain experienced by individuals with HS.
Friction and Skin Damage
Friction and repeated skin damage in areas affected by hidradenitis suppurativa can exacerbate pain. The condition typically affects regions where skin rubs together, such as the armpits and groin, leading to increased irritation. Activities that cause friction, such as physical exercise or wearing tight clothing, can worsen symptoms by irritating already inflamed skin. This additional damage can lead to increased pain and discomfort, making it essential for individuals with HS to manage their activities and avoid irritants whenever possible.
Immune System Response
An overactive or dysfunctional immune system plays a crucial role in the pain associated with hidradenitis suppurativa. HS is considered an autoinflammatory condition, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. This inappropriate immune response leads to chronic inflammation and pain. The release of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 (IL-1), contributes to the inflammatory process and subsequent pain. The complex interplay between immune dysregulation and pain in HS underscores the importance of targeting immune system activity in treatment strategies.
Pressure and Tenderness
HS lesions are often tender to the touch due to the underlying inflammation and swelling. The pressure from clothing or physical contact can exacerbate pain by putting additional strain on already inflamed tissues. The tenderness is a result of increased sensitivity in the affected areas, where even light touch can trigger pain. Understanding this sensitivity is important for managing pain and avoiding activities or garments that may worsen the discomfort.
Associated Complications
Several complications can contribute to increased pain in hidradenitis suppurativa. Secondary infections can occur when abscesses become infected, leading to further inflammation and pain. Scarring from chronic lesions can also cause discomfort, as scar tissue may be less flexible and more sensitive than normal skin. These complications can complicate the management of HS and require additional medical attention to address both the primary symptoms and associated issues.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain associated with hidradenitis suppurativa involves a multi-faceted approach. Medical treatments may include pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), to reduce discomfort. Anti-inflammatory medications and biologic therapies targeting specific inflammatory pathways can also be effective in managing pain. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding irritants, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and maintaining good hygiene, can help minimize friction and inflammation. Other pain relief methods, such as warm compresses or topical treatments, may provide additional comfort.
Psychological Impact
Chronic pain from hidradenitis suppurativa can significantly impact mental health and overall well-being. The persistent discomfort and visible symptoms of HS can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression. Coping with chronic pain involves addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition. Support from mental health professionals, stress management techniques, and counseling can be beneficial in managing the psychological impact of chronic pain.
Understanding why hidradenitis suppurativa hurts is crucial for effectively managing the condition and improving quality of life. By addressing the inflammatory process, immune system response, and other contributing factors, individuals with HS can take proactive steps to alleviate pain and enhance their overall well-being.
Realted Topics: