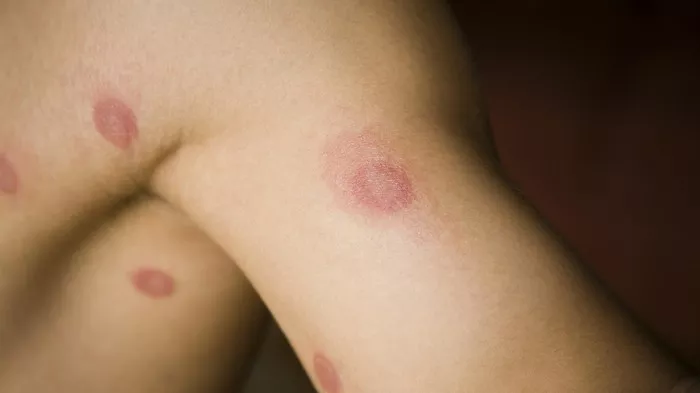
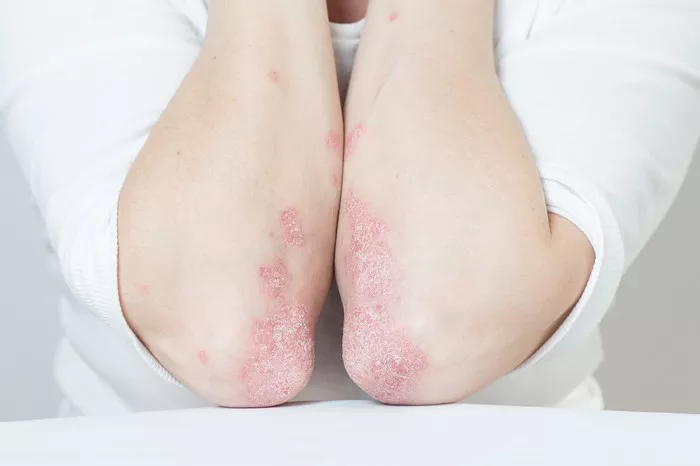
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches. It affects millions of people worldwide, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe irritation. While there is no cure for eczema, various over-the-counter (OTC) treatments can help manage its symptoms effectively.
Understanding Eczema:
Before delving into over-the-counter treatments, it’s crucial to grasp the basics of eczema. This condition stems from a combination of genetic and environmental factors, leading to inflammation and hypersensitivity of the skin. Common triggers include allergens, irritants, stress, climate changes, and certain foods. Eczema often presents in infancy and childhood but can persist into adulthood or manifest later in life.
Symptoms of eczema typically include:
1. Dry, itchy skin: The hallmark symptom of eczema is intense itching, which can lead to scratching and further skin damage.
2. Redness and inflammation: Affected areas of the skin may appear red, inflamed, and swollen.
3. Rash or patches: Eczema commonly presents as patches of rough, scaly skin or as a rash.
4. Thickened skin: In chronic cases, the skin may become thickened and leathery due to repeated scratching and irritation.
Managing Eczema with Over-the-Counter Treatments:
While severe cases of eczema may require prescription medications and specialized treatments, many individuals find relief from OTC options. These treatments aim to soothe itching, reduce inflammation, hydrate the skin, and repair the skin barrier. Here are some commonly used OTC treatments for eczema:
1. Moisturizers:
Keeping the skin well-hydrated is crucial for managing eczema. Moisturizers help trap moisture in the skin, preventing dryness and reducing itching. Opt for thick, fragrance-free creams or ointments, as they provide better hydration and are less likely to irritate sensitive skin. Ingredients like ceramides, glycerin, and hyaluronic acid are particularly beneficial for restoring the skin barrier.
2. Topical Corticosteroids:
Corticosteroid creams or ointments are widely used to alleviate inflammation and itching associated with eczema. These medications work by reducing immune responses in the skin and can provide rapid relief from symptoms. However, they should be used sparingly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as prolonged use can lead to thinning of the skin and other side effects.
3. Antihistamines:
Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine or cetirizine, can help relieve itching and promote better sleep for individuals with eczema. While they do not directly treat the underlying cause of eczema, they can provide temporary relief from symptoms, especially during flare-ups.
4. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors:
Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are non-steroidal medications that help reduce inflammation and itching in eczema-prone skin. These medications are particularly useful for sensitive areas of the body, such as the face and neck, where corticosteroids may be too harsh.
5. Colloidal Oatmeal Baths:
Colloidal oatmeal is a natural ingredient known for its soothing properties. Adding colloidal oatmeal to bathwater can help relieve itching, reduce inflammation, and soften the skin. Oatmeal baths are gentle enough for daily use and can provide significant relief for individuals with eczema.
6. Wet Wrap Therapy:
Wet wrap therapy involves applying moisturizer or medicated creams to the skin and then covering the affected areas with damp bandages or clothing. This technique helps lock in moisture, enhance the effectiveness of topical treatments, and soothe irritated skin. Wet wrap therapy is often recommended for severe eczema or during flare-ups.
7. Barrier Repair Creams:
Barrier repair creams contain ingredients like ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids, which help repair and strengthen the skin barrier. By restoring the skin’s natural protective barrier, these creams can reduce moisture loss, prevent irritants from entering the skin, and promote healing in eczema-prone skin.
8. Bathing and Hygiene Products:
Choosing gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and bathing products is essential for individuals with eczema. Harsh soaps and cleansers can strip the skin of its natural oils and exacerbate dryness and irritation. Look for mild, hypoallergenic formulas that are suitable for sensitive skin.
9. Cold Compresses:
Applying cold compresses or ice packs to itchy skin can provide immediate relief by numbing nerve endings and reducing inflammation. Cold therapy is a simple yet effective way to alleviate itching and discomfort associated with eczema flare-ups.
10. Humidifiers:
Dry indoor air can worsen eczema symptoms by dehydrating the skin. Using a humidifier in your home can help maintain optimal humidity levels, preventing dryness and reducing the likelihood of eczema flare-ups. Be sure to clean your humidifier regularly to prevent mold and bacteria growth.
It’s important to note that while OTC treatments can provide significant relief for many individuals with eczema, they may not be sufficient for severe or persistent cases. If symptoms worsen or do not improve with OTC treatments, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing eczema requires a multifaceted approach that addresses inflammation, itching, hydration, and skin barrier function. Over-the-counter treatments play a crucial role in this management strategy, providing accessible and effective options for symptom relief. By understanding the available OTC treatments and incorporating them into a comprehensive skincare routine, individuals with eczema can experience improved comfort and quality of life.