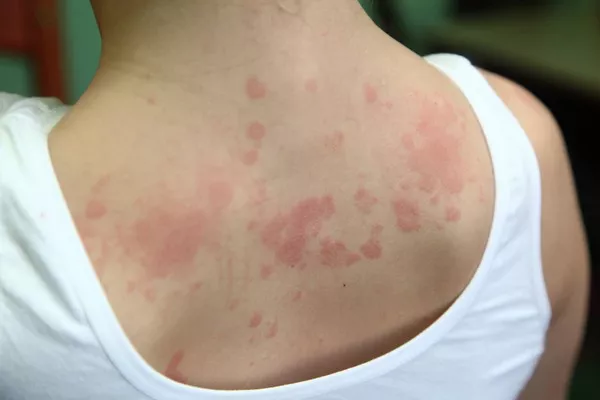
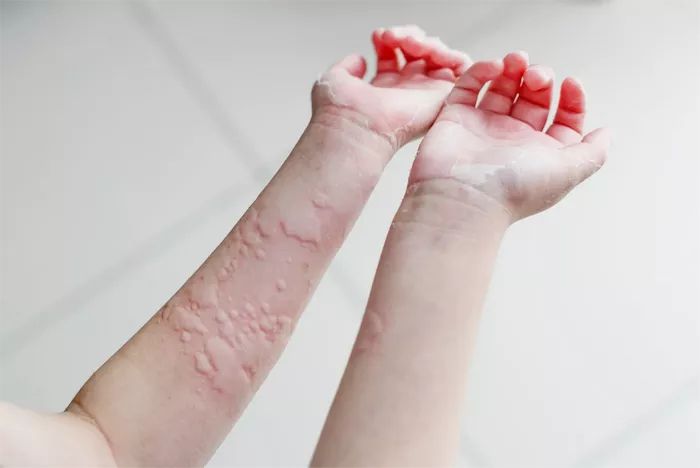
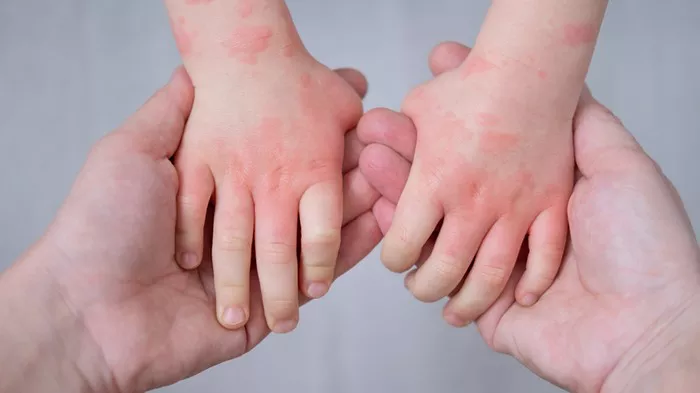
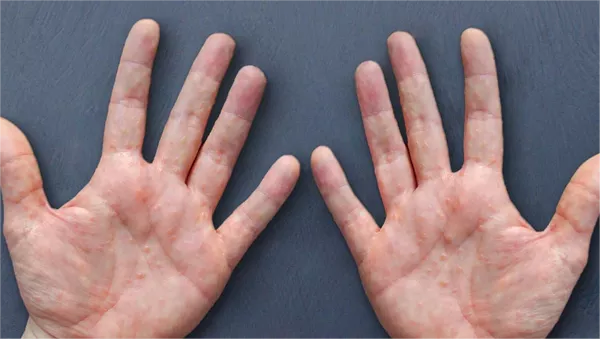
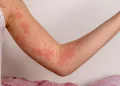
Refractory urticaria, a condition marked by persistent and resistant hives, poses significant challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. Characterized by chronic, often debilitating symptoms that fail to respond to conventional treatments, refractory urticaria necessitates a deeper understanding of its pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management options. This comprehensive article delves into the complexities of refractory urticaria, exploring its clinical features, underlying mechanisms, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies.
Introduction to Urticaria
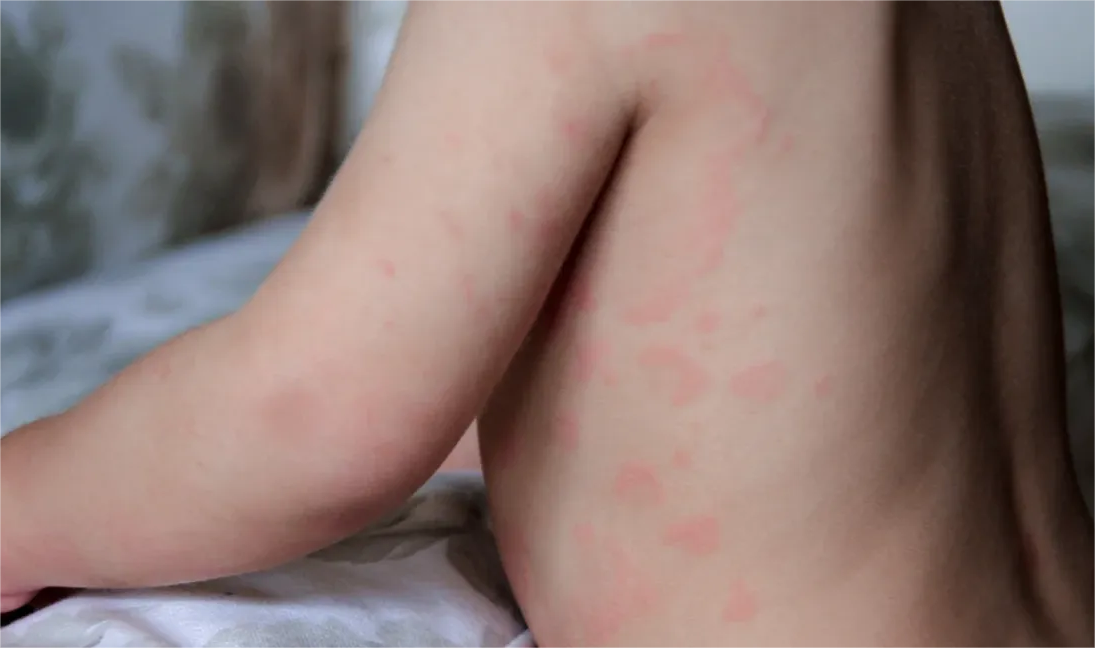
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a frequent dermatological condition characterized by transient, pruritic wheals or plaques. These lesions typically resolve within 24 hours but can recur over weeks or months. Urticaria is broadly classified into acute and chronic forms. Acute urticaria lasts less than six weeks and is often triggered by identifiable factors such as infections, allergens, or medications. Chronic urticaria, on the other hand, persists for more than six weeks and is subdivided into chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) and chronic inducible urticaria (CIU).
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
CSU occurs without any identifiable external triggers, making it particularly challenging to manage. Patients experience daily or almost daily hives and/or angioedema (deep tissue swelling) for an extended period. The unpredictability and persistence of symptoms significantly impact the quality of life, often leading to psychological distress.
Chronic Inducible Urticaria
CIU, unlike CSU, is triggered by specific physical stimuli such as pressure, cold, heat, exercise, or sunlight. The diagnosis is usually more straightforward due to the identifiable nature of the triggers.
Defining Refractory Urticaria
Refractory urticaria refers to cases of CSU or CIU that do not respond adequately to standard treatment regimens. Standard treatment typically involves second-generation H1-antihistamines at licensed doses, with an increase to up to four times the standard dose if necessary. Refractory urticaria is diagnosed when patients continue to experience significant symptoms despite these therapeutic interventions.
SEE ALSO: The 5 Best Over-the-Counter Antihistamines for Hives
Pathophysiology of Refractory Urticaria
The exact pathophysiological mechanisms underlying refractory urticaria remain incompletely understood, but several factors are thought to contribute:
Autoimmune Component
Autoimmune mechanisms play a critical role in many cases of refractory urticaria. Autoantibodies targeting the high-affinity IgE receptor (FcεRI) on mast cells and basophils or directly against IgE can lead to persistent activation and degranulation of these cells, releasing histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
Cellular Dysfunction
Mast cells and basophils, key effector cells in urticaria, may exhibit abnormal responses in refractory cases. Enhanced sensitivity or resistance to regulatory signals can perpetuate the inflammatory response. Additionally, dysregulated cytokine profiles, with elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α, have been implicated in refractory cases.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Genetic predisposition may influence the susceptibility to refractory urticaria. Variations in genes related to immune regulation, mast cell function, and inflammatory pathways can contribute to the chronicity and refractoriness of the condition. Environmental factors, including stress, infections, and dietary components, may also exacerbate symptoms and complicate management.
Clinical Features and Impact
Refractory urticaria presents with similar clinical features to other forms of chronic urticaria but with greater persistence and severity. Patients typically report:
Persistent Pruritus
Intense itching is a hallmark of urticaria, significantly affecting daily activities and sleep. In refractory cases, pruritus is often severe and unresponsive to antihistamines, necessitating additional therapeutic strategies.
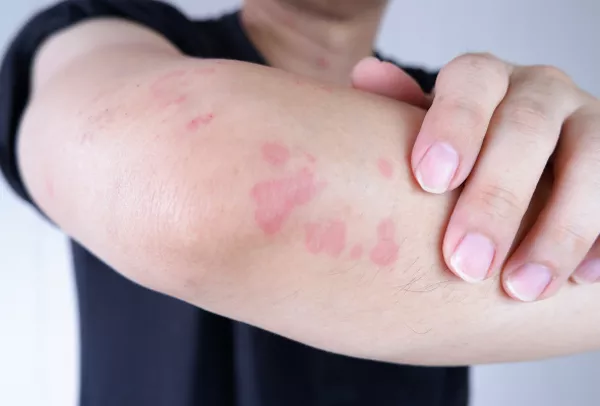
Recurrent Wheals and Angioedema
Patients experience frequent and widespread wheals, often accompanied by angioedema. The unpredictable nature of these symptoms contributes to psychological stress and reduced quality of life.
Psychological Distress
The chronic and refractory nature of the condition can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. The constant discomfort and appearance of the skin lesions can also affect self-esteem and interpersonal relationships.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing refractory urticaria involves a thorough clinical evaluation to rule out underlying causes and assess disease activity and severity. Key diagnostic steps include:
Detailed Patient History
A comprehensive history helps identify potential triggers, coexisting conditions, and previous treatment responses. This information is crucial for tailoring management strategies.
Physical Examination
A careful examination can reveal characteristic wheals and angioedema, providing clues about the subtype and severity of urticaria.
Laboratory Tests
Basic laboratory tests such as complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests, and thyroid function tests are often performed to exclude systemic causes. In cases with suspected autoimmune involvement, tests for autoantibodies (e.g., antithyroid antibodies) may be indicated.
Autologous Serum Skin Test (ASST)
ASST is a diagnostic tool used to detect autoantibodies in CSU. A small amount of the patient’s serum is injected intradermally, and the response is observed. A positive result suggests an autoimmune component, guiding further management.
Basophil Activation Test (BAT)
BAT measures the activation of basophils in response to stimuli, providing insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying refractory urticaria. This test can help identify patients with functional autoantibodies or other cellular abnormalities.
SEE ALSO: What Food Causes Hives on Skin
Management Strategies
Managing refractory urticaria requires a multifaceted approach, combining pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. The goal is to achieve symptom control, improve quality of life, and minimize side effects.
Pharmacological Treatments
Second-Generation H1-Antihistamines
These are the first-line treatment for chronic urticaria. In refractory cases, the dose may be increased up to fourfold. Common options include cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine. While generally well-tolerated, higher doses may cause sedation in some patients.
H2-Antihistamines
Adding an H2-antihistamine such as ranitidine can provide additional relief by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach and reducing overall histamine levels.
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
Drugs like montelukast can be beneficial for patients with refractory urticaria, particularly those with coexisting asthma or other allergic conditions. They work by inhibiting leukotrienes, inflammatory mediators involved in the pathogenesis of urticaria.
Corticosteroids
Short courses of oral corticosteroids may be used for acute exacerbations. However, long-term use is discouraged due to significant side effects such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased infection risk.
Immunomodulatory Agents
For severe refractory cases, immunomodulatory therapies may be considered:
- Omalizumab: This monoclonal antibody targets IgE and has shown efficacy in treating refractory CSU. It is administered subcutaneously and can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Cyclosporine: An immunosuppressant that inhibits T-cell activity, cyclosporine can be effective in refractory urticaria. However, its use is limited by potential nephrotoxicity and other adverse effects.
- Methotrexate: Low-dose methotrexate may benefit some patients by modulating the immune response and reducing inflammation.
Biologic Therapies
Emerging biologic therapies targeting specific pathways involved in urticaria are under investigation. These include ligelizumab (an anti-IgE antibody) and dupilumab (an IL-4 receptor antagonist). Clinical trials are ongoing to assess their efficacy and safety in refractory urticaria.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Avoidance of Triggers
Identifying and avoiding known triggers can help manage symptoms. Patients are advised to keep a symptom diary to track potential triggers such as foods, medications, or environmental factors.
Stress Management
Stress is a known exacerbating factor for urticaria. Techniques such as mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and relaxation exercises can help reduce stress levels and improve symptom control.
Dietary Modifications
While the role of diet in urticaria is not fully understood, some patients may benefit from dietary changes. A low-histamine diet or avoidance of specific foods identified as triggers can be helpful in certain cases.
Supportive Care
Patient Education
Educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and self-management strategies is crucial. Empowering patients with knowledge can enhance adherence to treatment and improve outcomes.
Psychological Support
Referral to a psychologist or counselor may be beneficial for patients experiencing significant psychological distress. Support groups and patient organizations can also provide valuable resources and a sense of community.
Future Directions and Research
Ongoing research into the pathophysiology and treatment of refractory urticaria holds promise for improved management strategies. Areas of focus include:
Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Monitoring
Identifying specific biomarkers associated with refractory urticaria can enhance diagnostic accuracy and allow for personalized treatment approaches. Biomarkers can also help monitor disease activity and treatment response.
Novel Therapeutics
The development of new therapeutic agents targeting specific pathways involved in urticaria offers hope for more effective treatments. Clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of various biologics and small molecules in refractory cases.
Understanding Genetic and Environmental Influences
Research into the genetic and environmental factors contributing to refractory urticaria can provide insights into disease mechanisms and potential prevention strategies. Understanding these influences may lead to targeted interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Refractory urticaria is a chronic form of hives that does not respond to standard treatments, including antihistamines and corticosteroids. This condition is characterized by persistent, itchy, and sometimes painful welts on the skin, which can significantly impact quality of life. Refractory urticaria can be challenging to manage due to its unpredictable nature and resistance to conventional therapies. Advanced treatments, such as omalizumab (a monoclonal antibody) or immunosuppressants, may be required. The exact cause of refractory urticaria is often unknown, but it may be related to autoimmune or other underlying systemic conditions.
Related Topics: