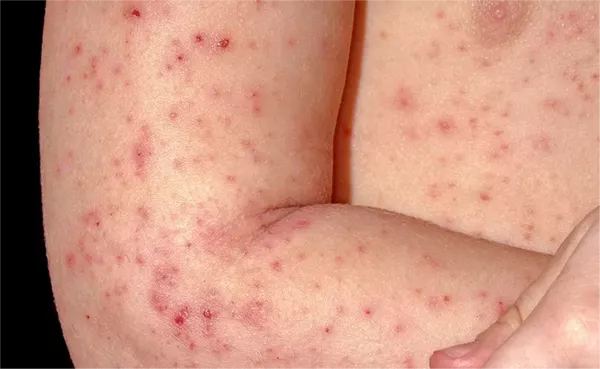
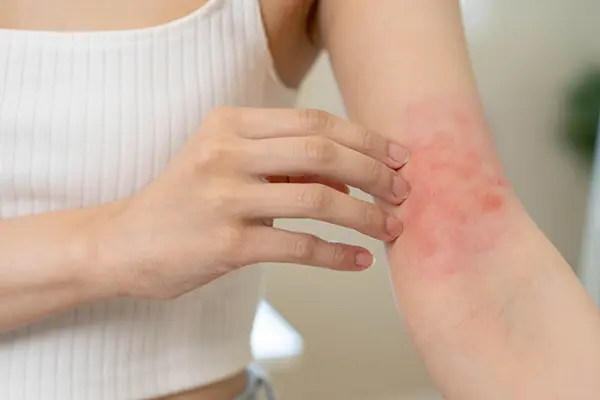
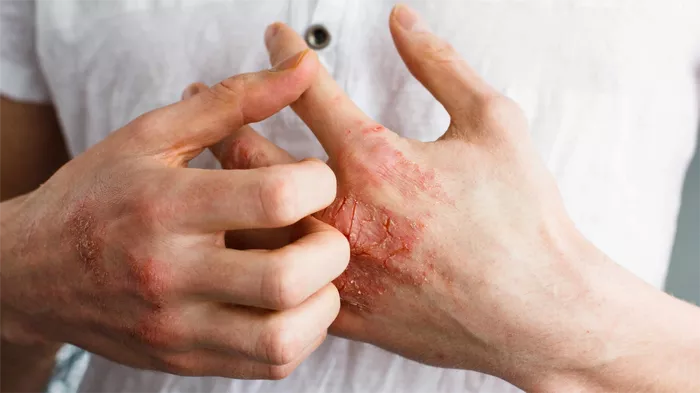
Papular eczema, a subtype of atopic dermatitis, is characterized by small, itchy, raised bumps on the skin. These papules can be extremely uncomfortable and may lead to secondary infections if not managed properly. Effective treatment requires a multifaceted approach, combining medical interventions, lifestyle changes, and preventative strategies. This article outlines the most effective methods for treating papular eczema, offering a detailed guide to managing this challenging skin condition.
Understanding Papular Eczema
Papular eczema manifests as tiny, raised bumps on the skin, often accompanied by redness, swelling, and intense itching. It can affect any part of the body, but is most commonly found on the arms, legs, and torso. The exact cause of papular eczema is not well understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The primary symptoms of papular eczema include:
- Small, raised bumps (papules) on the skin
- Severe itching, which can lead to scratching and skin damage
- Redness and swelling around the affected areas
- Dry, scaly patches of skin
Possible oozing or crusting if the papules are scratched and infected
Diagnosing papular eczema typically involves a physical examination by a dermatologist, who will look for characteristic signs of the condition. In some cases, a skin biopsy or allergy testing may be necessary to rule out other conditions and identify potential triggers.
Medical Treatments for Papular Eczema
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are often the first line of treatment for papular eczema. These anti-inflammatory medications help reduce redness, swelling, and itching. They come in various strengths, ranging from mild over-the-counter options to potent prescription formulations.
- Application: Apply a thin layer to the affected areas once or twice daily, as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Side Effects: Potential side effects include skin thinning, discoloration, and stretch marks with prolonged use. It is important to follow the prescribed duration and avoid overuse.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are non-steroidal options that help modulate the immune response in the skin. These medications are particularly useful for sensitive areas like the face and neck.
- Application: Apply a thin layer to the affected areas twice daily.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include burning or stinging sensations upon application. Long-term safety is still being studied, but they are generally considered safe for intermittent use.
Systemic Treatments
For severe cases of papular eczema that do not respond to topical treatments, systemic medications may be necessary. These include:
- Oral Corticosteroids: Used for short-term flare management. Long-term use is not recommended due to significant side effects.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications such as cyclosporine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil can help control severe eczema but require regular monitoring due to potential side effects.
- Biologics: Newer treatments like dupilumab target specific pathways in the immune system and have shown promise in treating severe eczema with fewer side effects.
Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can help reduce itching, especially at night. Non-sedating options like loratadine or cetirizine are preferred during the day, while sedating antihistamines like diphenhydramine may be used at night.
Antibiotics
If the papules become infected, a course of antibiotics may be necessary. This can be either topical (for localized infections) or oral (for widespread or severe infections).
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Moisturization
Keeping the skin well-moisturized is crucial for managing papular eczema. Emollients and moisturizers help restore the skin barrier and prevent dryness, which can exacerbate itching and inflammation.
- Frequency: Apply moisturizers at least twice daily, and immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Types: Look for products that are fragrance-free, hypoallergenic, and designed for sensitive skin. Ointments and creams are generally more effective than lotions.
Bathing Practices
Proper bathing techniques can help manage eczema symptoms:
- Lukewarm Baths: Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, so opt for lukewarm water.
- Short Duration: Limit baths to 10-15 minutes.
- Mild Cleansers: Use gentle, soap-free cleansers to avoid irritating the skin.
- Pat Dry: After bathing, gently pat the skin dry with a soft towel and immediately apply moisturizer.
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers can help reduce flare-ups. Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and certain foods.
- Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, and fabrics like wool.
- Climate: Extreme temperatures and humidity levels can aggravate eczema. Using a humidifier in dry conditions can be helpful.
- Stress: Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help reduce eczema flare-ups.
Diet and Nutrition
While there is no specific diet for eczema, certain foods may trigger symptoms in some individuals. Keeping a food diary can help identify potential triggers. Anti-inflammatory diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may benefit overall skin health.
SEE ALSO: How to Treat Sun Eczema
Preventative Strategies
Regular Skincare Routine
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine can help prevent flare-ups:
- Daily Moisturization: Regular use of moisturizers can keep the skin barrier intact.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing soft, breathable fabrics and protecting the skin from harsh weather conditions can reduce irritation.
Allergen Avoidance
For those with known allergies, taking steps to minimize exposure can prevent eczema flare-ups:
- Dust Mite Control: Use allergen-proof bedding covers and wash bedding in hot water weekly.
- Pet Dander: Keep pets out of the bedroom and regularly clean living areas.
- Pollen: During high pollen seasons, keep windows closed and use air purifiers.
Education and Support
Education about eczema and support from healthcare providers, family, and eczema support groups can be invaluable. Understanding the condition, its triggers, and management strategies can empower patients to take control of their symptoms.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial ultraviolet light. This can reduce inflammation and itching in moderate to severe cases of eczema.
- Types: Narrowband UVB is the most common form of phototherapy for eczema.
- Supervision: Treatment should be supervised by a dermatologist to minimize risks and monitor progress.
Herbal Remedies
Some herbal remedies have been traditionally used to manage eczema symptoms, although scientific evidence is limited. These include:
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing properties, aloe vera gel can be applied to affected areas.
- Chamomile: Chamomile creams or compresses may reduce inflammation and itching.
- Coconut Oil: Its moisturizing properties can help maintain the skin barrier.
Probiotics
Probiotics, beneficial bacteria found in supplements and fermented foods, may help improve eczema symptoms by modulating the immune system. Research is ongoing, but some studies suggest that certain strains of probiotics can reduce the severity of eczema.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting fine needles into specific points on the body. Some studies suggest it may help reduce itching and inflammation in eczema patients, but more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Conclusion
Treating papular eczema requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and preventative strategies. By combining these methods, individuals with papular eczema can manage their symptoms effectively and improve their quality of life. Regular consultation with healthcare providers, staying informed about new treatments, and adopting a proactive approach to skin care are essential steps in managing this chronic condition.
Related Topics: