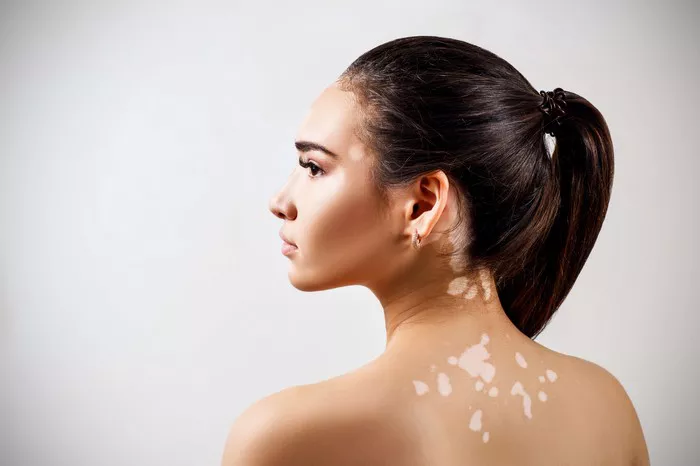
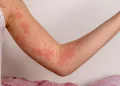
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition characterized by the loss of pigment, resulting in white patches on various parts of the body. This condition can affect individuals of all skin types, but it tends to be more noticeable in those with darker skin. While vitiligo’s exact cause is still not fully understood, it is widely recognized as an autoimmune disorder. Among the various countries studied for vitiligo prevalence, India stands out with the highest reported cases. This article delves into the epidemiology of vitiligo in India, examining potential causes, societal impact, and management strategies.
The Epidemiology of Vitiligo in India
India reports the highest prevalence of vitiligo globally, with studies indicating that approximately 0.5% to 2% of the population is affected, though some estimates suggest it could be as high as 8% in certain regions. This rate is significantly higher compared to the global average, which ranges from 0.1% to 2%. The variability in prevalence within India itself is attributed to genetic, environmental, and perhaps sociocultural factors that are unique to different regions of the country.
Possible Causes of High Vitiligo Prevalence in India
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in the incidence of vitiligo. Family history is a significant risk factor, with studies indicating that about 20% of vitiligo patients have a relative with the condition. In India, certain genetic markers associated with vitiligo have been identified more frequently, suggesting a hereditary component. Specific genes such as NLRP1 and PTPN22, known to be involved in autoimmune responses, are implicated in the development of vitiligo and are prevalent in the Indian population.
Environmental Factors
India’s unique environmental conditions may also contribute to the higher prevalence of vitiligo. Factors such as exposure to industrial chemicals, significant variations in climate, and dietary influences are considered potential triggers. For instance, oxidative stress due to high pollution levels in urban areas could play a role in the onset of vitiligo by damaging melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigment production.
Autoimmune Hypothesis
Vitiligo is widely recognized as an autoimmune disorder where the immune system erroneously attacks melanocytes. The high prevalence of autoimmune disorders in India, such as thyroid diseases, which are often comorbid with vitiligo, supports this hypothesis. The interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers may exacerbate the immune system’s response, leading to higher rates of vitiligo.
Societal and Psychological Impact
Stigma and Discrimination
In India, the societal impact of vitiligo is profound. There is a significant social stigma associated with the condition, often resulting in discrimination and social ostracization. In some parts of the country, vitiligo is mistakenly associated with leprosy, further intensifying the stigma. This misconception can lead to severe social and psychological consequences for those affected, including reduced marriage prospects, social isolation, and decreased self-esteem.
Psychological Distress
The psychological burden of vitiligo in India is substantial. Affected individuals often experience anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues due to their appearance and the associated societal reactions. Studies have shown that the quality of life for vitiligo patients in India is considerably lower compared to the general population, highlighting the need for comprehensive psychological support alongside medical treatment.
Management and Treatment Approaches
Medical Treatments
The treatment of vitiligo in India involves a range of medical therapies aimed at restoring skin color and halting the progression of the disease. Common treatments include:
- Topical Corticosteroids: These are often the first line of treatment for localized vitiligo, helping to reduce inflammation and promote repigmentation.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Used as an alternative to corticosteroids, especially on sensitive areas like the face and neck, to reduce inflammation without the side effects associated with steroids.
- Phototherapy: Narrowband UVB (NBUVB) therapy is a widely used treatment in India, known for its efficacy in stimulating melanocyte activity and repigmentation.
- Surgical Options: For stable vitiligo, surgical procedures such as melanocyte transplants or skin grafting are considered. These methods are particularly prevalent in specialized dermatological centers across India.
SEE ALSO: What Are Signs of Vitiligo
Traditional and Alternative Medicine
In addition to conventional medical treatments, traditional and alternative medicine plays a significant role in managing vitiligo in India. Ayurvedic treatments, which include herbal remedies and dietary modifications, are popular among patients seeking holistic approaches. These treatments focus on balancing the body’s doshas (energy forces) and are believed to improve overall health and skin condition.
Psychological Support and Counseling
Given the significant psychological impact of vitiligo, integrating psychological support into the treatment regimen is crucial. Counseling and support groups can help patients cope with the emotional stress and societal stigma associated with the condition. Initiatives to raise awareness and educate the public about vitiligo can also reduce stigma and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Public Health Initiatives and Awareness Campaigns
Government and Non-Governmental Efforts
Both governmental and non-governmental organizations in India have initiated various programs to address the challenges faced by vitiligo patients. Public health campaigns aim to educate the population about the condition, dispel myths, and reduce stigma. These efforts include workshops, seminars, and media campaigns designed to increase awareness and understanding of vitiligo.
Vitiligo Support Organizations
Several support organizations in India provide resources, advocacy, and community for those affected by vitiligo. These organizations work to improve access to treatment, offer psychological support, and promote research into the condition. By fostering a supportive environment, they help patients navigate the social and emotional challenges associated with vitiligo.
Research and Future Directions
Genetic and Clinical Research
Ongoing research in India aims to uncover more about the genetic basis of vitiligo and improve treatment options. Studies focusing on the genetic predisposition and molecular mechanisms underlying the condition are crucial for developing targeted therapies. Clinical trials for new medications and treatment protocols are also an important aspect of advancing vitiligo management.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in medical technology, such as the development of more effective phototherapy devices and innovative surgical techniques, hold promise for improving treatment outcomes for vitiligo patients in India. Additionally, mobile health (mHealth) applications that provide information, track treatment progress, and connect patients with healthcare providers are emerging tools that can enhance patient care.
Conclusion
Vitiligo is a significant dermatological condition in India, affecting a notable portion of the population and carrying profound social and psychological implications. The higher prevalence in India compared to other regions highlights the need for a multifaceted approach to address the condition. By integrating medical treatment, traditional medicine, psychological support, and public health initiatives, India can better support those affected by vitiligo. Continued research and technological advancements will also play a critical role in improving understanding and management of this complex condition. Through these combined efforts, the stigma associated with vitiligo can be reduced, and the quality of life for patients can be significantly improved.
Related Topics: