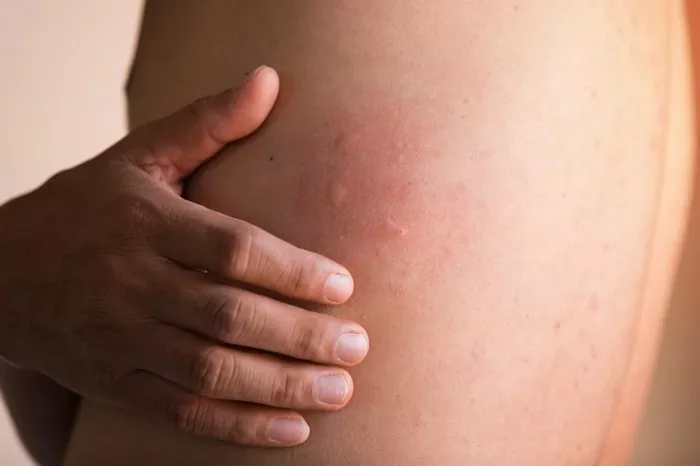
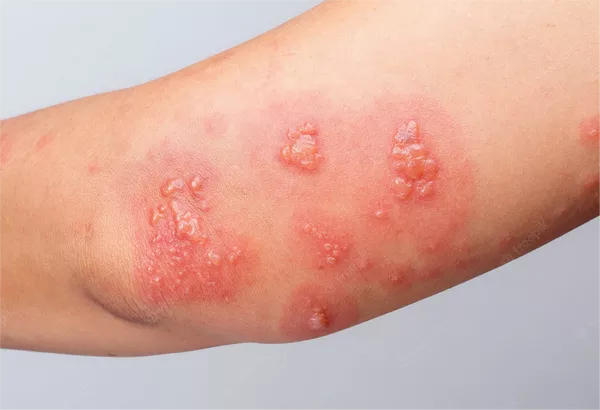
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and swollen welts on the skin. These welts can vary in size and shape, often appearing suddenly and disappearing just as quickly. While hives can be caused by various triggers, including allergens, stress, infections, and medications, the exact cause often remains unknown in many cases. When hives become chronic or severe, it is crucial to seek medical attention. This article explores the various ways doctors can assist patients suffering from hives, from diagnosis to treatment and management.
Diagnosis of Hives
1. Initial Consultation and History Taking
The first step a doctor takes in managing hives is to conduct a thorough patient history and physical examination. During the initial consultation, the doctor will ask about:
- The onset and duration of hives
- Possible triggers (e.g., foods, medications, insect stings, or stress)
- Frequency and pattern of occurrence
- Associated symptoms (e.g., fever, difficulty breathing, or abdominal pain)
- Personal and family medical history, including any history of allergies or autoimmune diseases
- This information helps the doctor identify potential causes and patterns, guiding further diagnostic steps.
2. Physical Examination
During the physical examination, the doctor will inspect the hives, noting their size, shape, distribution, and any signs of infection or complications. This examination helps differentiate hives from other skin conditions with similar presentations, such as eczema, psoriasis, or insect bites.
3. Allergy Testing
If an allergic reaction is suspected as the cause of hives, the doctor may recommend allergy testing. This can include:
- Skin Prick Tests: Small amounts of potential allergens are introduced into the skin using a needle. If the patient is allergic to a substance, a localized hive will form at the test site.
- Blood Tests: These tests measure specific IgE antibodies in the blood, which indicate an allergic response to certain substances.
4. Laboratory Tests
In some cases, additional laboratory tests may be necessary to rule out underlying conditions or infections. These tests can include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check for signs of infection or inflammation.
- Thyroid Function Tests: To rule out thyroid disorders, which can be associated with chronic hives.
- Autoimmune Panel: To check for autoimmune diseases, which can sometimes cause chronic hives.
Treatment Options for Hives
1. Avoidance of Triggers
One of the primary strategies in managing hives is identifying and avoiding known triggers. Once the doctor has identified potential triggers, they will provide guidance on how to avoid them. For example:
- If certain foods are identified as triggers, the patient may need to follow an elimination diet.
- If medications are the cause, alternatives may be prescribed.
- For environmental triggers, steps can be taken to reduce exposure, such as using air purifiers for dust mites or avoiding outdoor activities during high pollen seasons.
2. Medications
Various medications are available to treat hives, depending on the severity and frequency of the symptoms.
Antihistamines: These are the first line of treatment for hives. They work by blocking histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction that causes itching and swelling. Common antihistamines include cetirizine, loratadine, and diphenhydramine. Non-sedating antihistamines are often preferred for daytime use.
Corticosteroids: For severe or persistent hives, short-term use of corticosteroids like prednisone may be prescribed. These medications reduce inflammation and immune response, providing relief from severe symptoms.
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: These medications, such as montelukast, can be used in conjunction with antihistamines to control symptoms in some patients.
Biologic Therapies: In cases of chronic hives that do not respond to standard treatments, biologic therapies like omalizumab (an anti-IgE antibody) may be considered. Omalizumab is administered via injection and can help reduce the severity and frequency of hives.
3. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, such as anti-itch creams and lotions containing menthol or camphor, can provide temporary relief from itching and discomfort. In some cases, topical corticosteroids may be prescribed for localized hives.
SEE ALSO: Does Scratching Hives Make Them Spread?
Management and Prevention of Hives
1. Long-term Management Strategies
For patients with chronic hives, long-term management strategies are essential. Doctors may recommend the following:
- Regular Follow-ups: Periodic visits to monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help reduce the frequency of hives triggered by stress.
- Dietary Adjustments: For patients with food-related hives, a dietitian may help develop a balanced diet that avoids known triggers.
2. Patient Education
Educating patients about their condition and how to manage it is a crucial aspect of treatment. Doctors should provide information on:
- Recognizing early signs of hives and knowing when to seek medical attention.
- Proper use of medications, including potential side effects and interactions.
Techniques for avoiding known triggers.
3. Emergency Preparedness
In rare cases, hives can be associated with severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis. Doctors should educate patients on recognizing the signs of anaphylaxis (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, rapid heartbeat) and the importance of having an emergency action plan. This plan may include carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) and knowing how to use it.
Special Considerations in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients
1. Pediatric Patients
Hives are common in children and can be particularly distressing for both the child and their parents. Pediatricians play a vital role in managing hives in this population by:
- Conducting age-appropriate allergy testing.
- Prescribing medications with a focus on safety and minimal side effects.
- Providing guidance on avoiding common pediatric triggers, such as certain foods or infections.
- Educating parents on how to manage symptoms at home and when to seek medical help.
2. Geriatric Patients
In elderly patients, hives can present unique challenges due to comorbidities and the potential for drug interactions. Geriatricians must:
- Carefully review the patient’s medication list to identify possible drug-induced hives.
- Choose treatment options that minimize the risk of side effects and interactions.
- Monitor for underlying conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, that may be more prevalent in this age group.
- Provide comprehensive care that addresses both the hives and any associated health issues.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research into the underlying mechanisms of hives and potential new treatments is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Some areas of current research include:
- Genetic Studies: Investigating genetic factors that may predispose individuals to hives.
- Immunological Research: Understanding the role of the immune system in the development of hives, particularly chronic cases.
- Novel Therapies: Developing new medications and biologics that target specific pathways involved in the inflammatory process.
As our understanding of hives continues to evolve, so too will the strategies for managing and treating this condition. Doctors play a key role in implementing these advancements to provide better care for their patients.
Conclusion
Hives can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, but with proper medical care, they can be effectively managed. From accurate diagnosis to individualized treatment plans and ongoing management, doctors have a range of tools and strategies to help patients with hives. By staying informed about the latest research and treatment options, doctors can continue to improve outcomes for their patients, providing relief and enhancing their quality of life.
Related Topics: