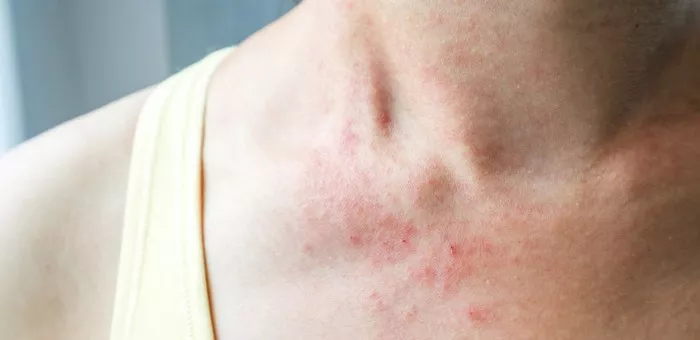
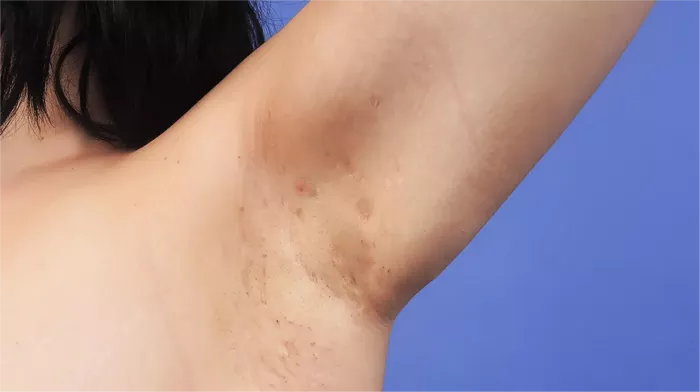
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition characterized by painful lumps under the skin, typically in areas where skin rubs together, like the armpits, groin, buttocks, and breasts. These lumps can become swollen, tender, and filled with pus, leading to abscesses, scarring, and tunnels under the skin. HS is often misunderstood and underdiagnosed, but it can have a significant impact on the quality of life of those who suffer from it.
What Are the Symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis suppurativa usually begins as small, firm bumps under the skin. These bumps can be red, painful, and tender. Over time, the condition may worsen, leading to more severe symptoms.
Painful Lumps: The first sign of HS is often small, painful lumps in areas where skin rubs against skin. These areas include the underarms, groin, inner thighs, and under the breasts.
Abscesses: As the condition progresses, the lumps can turn into abscesses. These abscesses are swollen, pus-filled areas that can burst and release a foul-smelling fluid.
Tunnels (Sinus Tracts): In severe cases, tunnels or sinus tracts can form under the skin, connecting different abscesses. These tunnels can make the condition more painful and increase the risk of infection.
Scarring: After the abscesses heal, the skin may scar. In some cases, these scars can become thick and raised, leading to further discomfort and mobility issues.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic condition, meaning it can last for years, and the symptoms may come and go. Some people experience flare-ups, where the symptoms become more intense for a period before subsiding.
What Causes Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is not fully understood. However, researchers believe that it may be related to inflammation and blockages of hair follicles in areas where sweat glands are concentrated. Some factors may contribute to the development of HS, including genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle elements.
1. Hair Follicle Blockages
One of the leading theories is that HS begins when hair follicles become blocked. When the hair follicle is blocked, inflammation occurs, which can cause swelling, infection, and abscess formation. This blockage may be triggered by friction, pressure, or sweating, especially in areas of the body where skin rubs against skin.
2. Inflammation
Hidradenitis suppurativa is considered an inflammatory skin disease. Inflammation occurs when the body’s immune system reacts to an infection or injury. In the case of HS, this immune response is often exaggerated, leading to painful swelling and pus formation under the skin.
3. Hormonal Factors
Hormonal changes may also play a role in the development of HS. The condition often begins after puberty and is more common in women than men, which suggests a hormonal link. Hormones like androgens (male hormones present in both men and women) may influence the onset or severity of the condition.
4. Genetic Factors
There is evidence that hidradenitis suppurativa may have a genetic component. Studies have shown that the condition can run in families, meaning that if a parent or sibling has HS, there is an increased likelihood that another family member may develop the condition as well.
5. Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking and being overweight, can increase the risk of developing hidradenitis suppurativa or worsen the condition in people who already have it. Both smoking and obesity are associated with higher levels of inflammation, which may contribute to the flare-ups and progression of HS.
Who Is at Risk of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis suppurativa can affect anyone, but certain factors increase the risk of developing the condition.
Age: HS often starts after puberty, typically between the ages of 20 and 40. It rarely occurs before puberty or in older adults.
Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop hidradenitis suppurativa. This may be related to hormonal differences, particularly during reproductive years.
Family History: People with a family history of HS have a higher risk of developing the condition, which suggests that genetics play a role.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of HS. Excess weight can lead to more skin friction and increased inflammation, both of which are linked to the development of the condition.
Smoking: Smoking is another risk factor for HS. The chemicals in cigarettes can promote inflammation, making it easier for the condition to develop or worsen.
How Is Hidradenitis Suppurativa Diagnosed?
Diagnosing hidradenitis suppurativa can be challenging because its symptoms can resemble other skin conditions, such as boils, cysts, or infections. A healthcare professional, usually a dermatologist, can diagnose HS based on the appearance of the skin and the patient’s medical history.
Physical Examination: A doctor will examine the affected areas of the skin and look for characteristic signs of HS, such as painful lumps, abscesses, and scarring.
Medical History: The doctor may ask questions about the patient’s family history, lifestyle habits (such as smoking or weight), and any previous skin conditions to determine if these factors are contributing to HS.
Imaging: In some cases, imaging tests like ultrasounds may be used to determine the extent of inflammation or to detect tunnels (sinus tracts) that may not be visible on the surface of the skin.
How Is Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treated?
There is no cure for hidradenitis suppurativa, but treatment can help manage the symptoms, reduce pain, and prevent the condition from worsening. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition and the specific needs of the patient.
1. Medications
Medications are often the first line of treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. These can help control inflammation, reduce infection, and promote healing.
Topical Antibiotics: Creams or ointments containing antibiotics can help treat mild cases of HS by reducing bacteria on the skin.
Oral Antibiotics: For more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to treat or prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
Corticosteroids: Steroid injections can be used to reduce swelling and pain in the affected areas.
Biologic Medications: Biologic drugs, such as adalimumab (Humira), are designed to target specific parts of the immune system and reduce inflammation. These medications are typically used for more severe cases of HS that do not respond to other treatments.
2. Surgery
In more advanced cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected tissue, drain abscesses, or prevent further complications.
Incision and Drainage: This procedure involves making a small cut to drain pus from an abscess. While this can provide relief, it is not a permanent solution, and abscesses may return.
Excision: In some cases, the doctor may recommend removing the affected skin and tissue. This is typically reserved for severe cases where the HS has caused significant damage.
Laser Surgery: Laser treatments can be used to remove hair follicles and reduce inflammation, which may help prevent future flare-ups.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency of HS flare-ups and improve overall quality of life.
Weight Management: Losing weight can reduce skin friction and lower the risk of inflammation, which may help prevent HS symptoms from worsening.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can reduce inflammation and improve overall skin health, potentially reducing the severity of HS.
Hygiene: Keeping the affected areas clean and dry, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and avoiding friction can help prevent irritation and reduce the risk of flare-ups.
Living with Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa can have a significant impact on a person’s physical and emotional well-being. Living with chronic pain, discomfort, and visible skin changes can lead to feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and social isolation.
1. Managing Pain and Discomfort
Pain is a common symptom of HS, and managing it is essential for improving quality of life. In addition to medications, applying warm compresses or taking over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort during flare-ups.
2. Emotional Support
Because hidradenitis suppurativa can affect self-esteem and mental health, it’s important for individuals to seek emotional support. Joining support groups, talking to a counselor, or connecting with others who have HS can provide comfort and help individuals cope with the challenges of the condition.
3. Regular Medical Care
Regular visits to a dermatologist or healthcare provider are important for managing HS and preventing complications. A doctor can monitor the progression of the condition, adjust treatment as needed, and provide advice on managing symptoms.
SEE ASLO: Does Hidradenitis Suppurativa Cause Cancer?
Conclusion
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can cause significant discomfort, pain, and scarring. While the exact cause of HS is not fully understood, factors like hair follicle blockages, inflammation, hormones, genetics, and lifestyle elements can all contribute to the condition.
Although there is no cure for HS, various treatments, including medications, surgery, and lifestyle changes, can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. By working closely with a healthcare provider and taking steps to reduce flare-ups, individuals with HS can find relief and lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges of the condition.
Related Topics: